Now Reading: Unifying Architecture and Design: Integrating C4 and UML with Visual Paradigm AI
-
01
Unifying Architecture and Design: Integrating C4 and UML with Visual Paradigm AI
Unifying Architecture and Design: Integrating C4 and UML with Visual Paradigm AI
In the complex landscape of software engineering, a persistent gap often exists between high-level architectural narratives and the granular technical specifications required for implementation. Architects typically focus on the broad structure and interactions of systems, while developers require precise details regarding classes, interfaces, and logic flows. Visual Paradigm’s AI-powered ecosystem bridges this gap by integrating the C4 model’s structural abstraction with UML’s detailed behavioral views. This comprehensive guide explores how Visual Paradigm utilizes AI to create a synergy between these two standards, allowing teams to define the system’s narrative while providing the necessary “fine print” for execution.
Bridging Architectural Narratives with Technical Implementation
The core philosophy behind integrating C4 and UML within Visual Paradigm is to provide a continuum of documentation. The C4 model excels at telling the story of the software—defining the context, containers, and components in a way that is accessible to stakeholders. Conversely, the Unified Modeling Language (UML) serves as the technical blueprint, offering the rigor required for actual coding. Visual Paradigm leverages AI to facilitate this connection, ensuring that the high-level vision defined in C4 diagrams flows logically into the detailed implementation views of UML.
Key Mechanisms of Integration in Visual Paradigm AI
Visual Paradigm employs several AI-driven mechanisms to ensure that the transition between architectural layers and detailed design is seamless and traceable. Below are the primary methods used to facilitate this integration.
1. Seamless Transition from Structure to Detail
One of the most powerful features of Visual Paradigm is the ability to move fluidly between abstraction levels. The platform’s AI Diagramming Chatbot and C4 AI Diagram Generator empower teams to rapidly generate high-level C4 diagrams, such as Context, Container, and Component views. Once the structural foundation is laid, users can seamlessly switch contexts to generate granular UML diagrams.
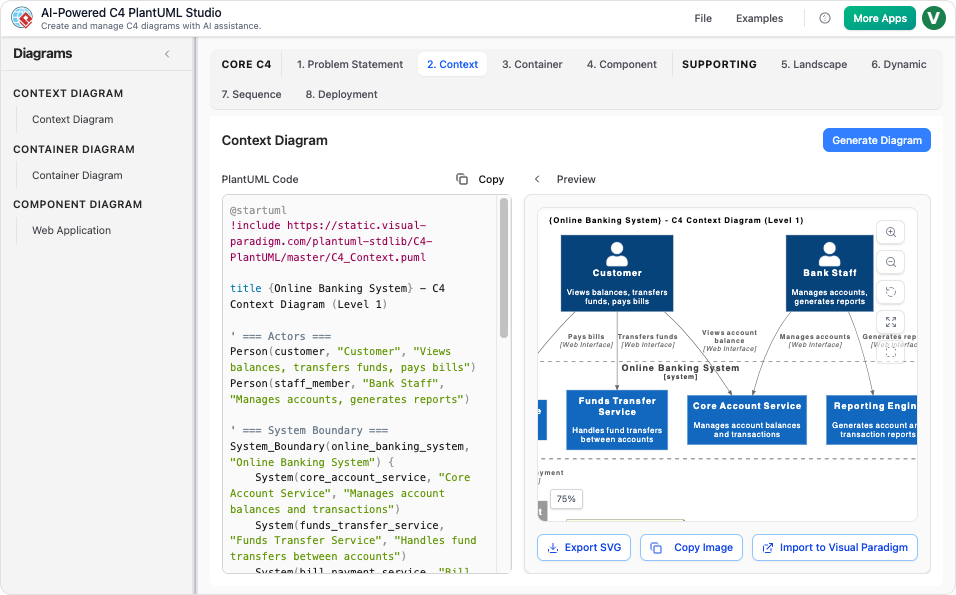
For instance, an architect might use the AI tools to generate a C4 Container diagram that outlines the major services of an application. From there, they can prompt the AI to instantly create a UML Sequence diagram. This transition transforms a static box-and-line representation of services into a detailed interaction flow, specifying exactly how those containers communicate during specific operations.
2. Modeling Runtime Behavior
While the C4 model includes Dynamic diagrams to illustrate high-level workflows, they often lack the precision required for debugging or implementation logic. Visual Paradigm solves this by distinguishing between broad process flows and exact message exchanges.
- C4 Dynamic View: This is used to visualize broad processes. For example, it might depict a “Checkout Process” showing the relationship between a “Frontend Application” and a “Payment Service.”
- UML Sequence View: Within the VP ecosystem, this view details the precise programmatic interactions. It moves beyond the conceptual link to show the Frontend calling specific methods, such as
PaymentService.processPayment(), followed by the subsequent return messages and database inventory updates.
3. Implementation at the Code Level (Level 4)
The C4 model hierarchy typically ends at the Component level, often referring to “Level 4” (Code) as an optional deep dive. Visual Paradigm formalizes this level by utilizing UML Class diagrams to document the internal structure of the components defined in C4.
In this workflow, a C4 Component diagram might identify a “Payment Service” component. The linked UML Class diagram then reveals the internal architecture of that component, detailing:
- Specific classes, interfaces, and their relationships.
- Attributes, method signatures, and inheritance hierarchies.
- The essential blueprint for objects like
PaymentProcessor,Transaction, andInvoice.
4. A Unified Modeling Environment
A significant challenge in mixed-model documentation is maintaining consistency. Because Visual Paradigm provides a single platform for both C4 and UML standards, it ensures strict consistency and traceability. Changes made to a component in a C4 diagram can be automatically reflected or linked to its corresponding representations in UML diagrams. This unified environment allows technical leads and business stakeholders to maintain a shared high-level vision, while developers work on the detailed design simultaneously without the risk of information drift.
Analogy: The Digital Camera Approach
To understand the power of this integration, consider the analogy of a high-end digital photography workflow. Integrating C4 and UML in Visual Paradigm is akin to using a professional camera system equipped with specialized lenses.
The C4 Model acts as your wide-angle lens. It captures the entire landscape, showing the horizon, the major landmarks, and how they relate to one another in the broader context. It provides the big picture necessary for orientation and strategy.
UML functions as your macro lens. It allows you to zoom in with extreme precision to observe the texture of a single leaf or the intricate internal gears of a clock. It reveals the mechanics that make the landscape functional.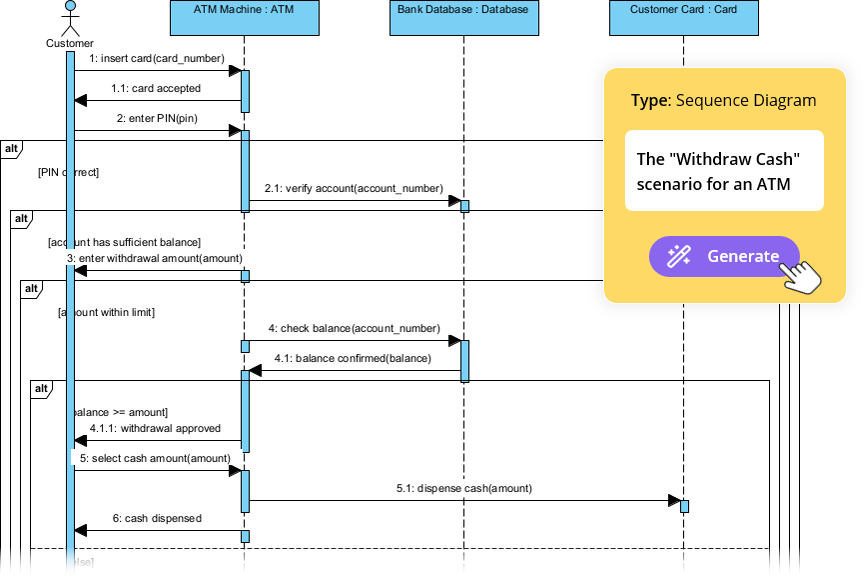
Visual Paradigm serves as the camera body. It is the sophisticated engine that allows you to switch between these lenses instantly. It ensures that whether you are shooting a panorama or a close-up, every image remains part of the same consistent photo album, sharing the same metadata and storage.
Summary Comparison
| Feature | C4 Model (Wide-Angle) | UML (Macro Lens) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Architectural Narrative & Context | Technical Specification & Implementation |
| Target Audience | Stakeholders, Architects, Product Managers | Developers, Engineers, QA |
| Visual Paradigm AI Role | Generating structure (Context/Container/Component) | Generating logic details (Sequence/Class/State) |
| Level of Detail | High-level abstraction | Method, Class, and Attribute precision |
-
Ultimate Guide to C4 Model Visualization Using Visual Paradigm’s AI Tools: A comprehensive guide on leveraging Visual Paradigm’s AI-powered tools to automate and enhance C4 model visualization for faster, smarter software architecture design.
-
Leveraging Visual Paradigm’s AI C4 Studio for Streamlined Architecture Documentation: A detailed guide on using Visual Paradigm’s AI-enhanced C4 Studio to create clean, scalable, and maintainable software architecture documentation.
-
The Ultimate Guide to C4-PlantUML Studio: Revolutionizing Software Architecture Design – Visual Paradigm Blog: 2 weeks ago – Software architecture documentation is often a bottleneck—time-consuming, error-prone, and quickly outdated. The C4-PlantUML Studio, developed by Visual Paradigm, changes this by combining AI-driven automation, the C4 model’s clarity, and PlantUML’s flexibility into a single, powerful tool.
-
A Comprehensive Guide to Visual Paradigm’s AI-Powered C4 …: Dec 3, 2025 · Enter Visual Paradigm ’s AI-Powered C4 PlantUML Studio, released November 14, 2025 — a purpose-built tool that transforms natural language into correct, layered C4 diagrams. But how is it different from just asking ChatGPT or Claude to “draw a system diagram”? And can it really generate valid C4? Let’s unpack it all.
-
C4-PlantUML Studio | AI-Powered C4 Diagram Generator – Visual Paradigm: An AI-powered tool to automatically generate C4 software architecture diagrams from simple text descriptions.
-
Comprehensive Tutorial: Generating and Modifying C4 Component …: Dec 16, 2025 · This tutorial is based on the official Visual Paradigm product demo video, demonstrating how to use the AI-powered Chatbot to create and iteratively refine a C4 Component Diagram for a car park booking system. The C4 model (Context, Containers, Components, and Code) is a popular approach for visualizing software architecture, and the Component level focuses on the internal structure of a …
-
AI-Powered C4 Diagram Generator – Visual Paradigm AI: C4 & Supporting Diagrams The AI-Powered C4 Diagram Generator supports the four core levels of the C4 Model (Context, Container, Component, Deployment) plus essential supporting views to provide comprehensive architectural documentation. Core C4 Diagrams The Core C4 Diagrams are fundamental for documenting the static structure of your software system, detailing how it is broken down …
-
Visual Paradigm Full C4 Model Support Release: This release announcement details the integration of full C4 model support in Visual Paradigm, enabling users to create and manage architecture diagrams at multiple abstraction levels.
-
New: Full C4 Model Support Added to Visual Paradigm Desktop – ArchiMetric: 6 days ago · The C4 Model: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Software Architecture with AI-Powered Tools …
-
Visual-paradigm: Our AI supports a wide range of diagrams across various domains, including UML, C4 models for software architecture, and strategic frameworks like SWOT and PESTLE analysis.
-
Visual Paradigm AI Suite: A Comprehensive Guide to Intelligent Modeling Tools – Cybermedian: 6 days ago – Strategic Frameworks: SWOT Analysis, PEST/PESTLE Analysis, Ansoff Matrix, and Blue Ocean Four Actions Framework. Systems Engineering: SysML Block Definition, Internal Block, and Requirement diagrams. Architecture: ArchiMate diagrams and C4 models. General Business: Organization Charts, Mind Maps, and PERT Charts. While the AI Chatbot is a cloud-based feature of VP Online, it is seamlessly integrated into the Visual Paradigm Desktop environment.
-
Visual-paradigm: Our AI supports a wide range of diagrams across various domains, including UML, C4 models for software architecture, and strategic frameworks like SWOT and PESTLE analysis.














