Now Reading: Mastering Strategic Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to AI-Powered SWOT and TOWS Frameworks
-
01
Mastering Strategic Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to AI-Powered SWOT and TOWS Frameworks
Mastering Strategic Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to AI-Powered SWOT and TOWS Frameworks
Introduction to Strategic Analysis in the Digital Age
In the rapidly evolving landscape of global business, the ability to adapt and respond to internal and external variables is paramount. Strategic planning frameworks, particularly the SWOT Analysis, have long served as the bedrock for decision-making. However, the traditional methods of manually drafting these analyses are often time-consuming and prone to cognitive bias. With the advent of artificial intelligence, strategic modeling has undergone a significant transformation.
This comprehensive guide explores the fundamentals of SWOT and TOWS analysis, delves into the mechanics of modern AI-powered tools, and demonstrates how Visual Paradigm’s ecosystem streamlines the transition from raw data to actionable business strategy.
Deconstructing the SWOT Framework
At its core, a SWOT Analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the competitive position of a company, project, or product. It provides a structured view of the landscape by categorizing factors into four distinct dimensions: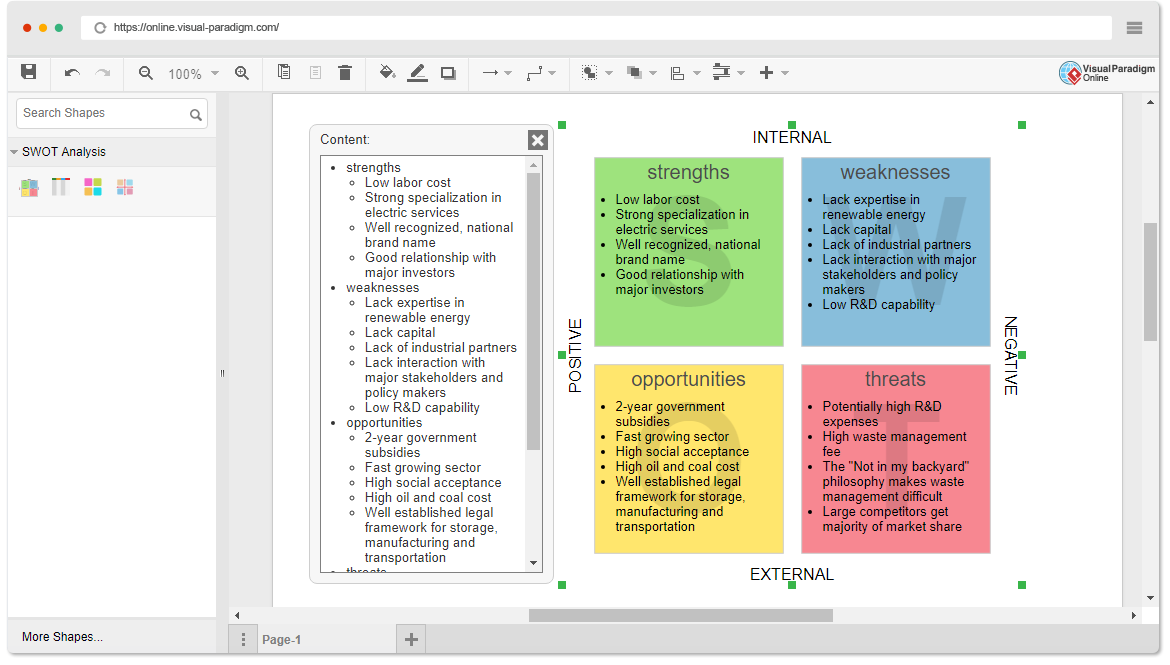
- Strengths (Internal): Capabilities and resources that give an organization a competitive advantage. Examples include a strong brand reputation, proprietary technology, or a skilled workforce.
- Weaknesses (Internal): Limitations or deficiencies that hinder performance. These might include budget constraints, outdated infrastructure, or a lack of specialized expertise.
- Opportunities (External): Favorable external factors that the organization can exploit for growth, such as emerging markets, regulatory changes, or technological advancements.
- Threats (External): External risks that could jeopardize success, including new competitors, economic downturns, or shifting consumer preferences.
Deep Dive: Analyzing Internal Factors
To conduct a thorough analysis, it is essential to look beyond surface-level attributes. Internal factors (Strengths and Weaknesses) generally revolve around specific operational pillars:
- Quality: Product safety, reliability, aesthetics, and durability.
- Price: Cost structures, profit margins, and competitive pricing strategies.
- Process: Production efficiency, supply chain stability, and delivery timelines.
- Capability: Talent density, management expertise, and R&D innovation cycles.
- Sales & Service: Network reach, customer loyalty, and after-sales support systems.
From Analysis to Action: The TOWS Matrix
While SWOT identifies the factors, the TOWS Matrix is the framework that operationalizes them. It forces strategists to move beyond simple listing and start connecting internal capabilities with external realities to form concrete strategies.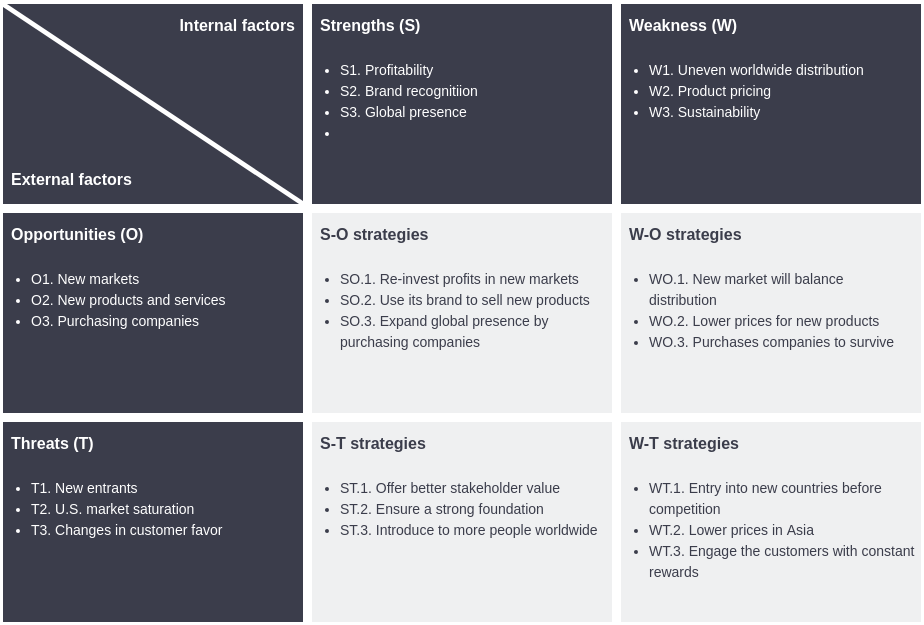
| Strategy Type | Description | Objective |
|---|---|---|
| SO Strategies (Maxi-Maxi) | Strengths + Opportunities | Use internal strengths to maximize external opportunities. |
| WO Strategies (Mini-Maxi) | Weaknesses + Opportunities | Overcome internal weaknesses by taking advantage of external opportunities. |
| ST Strategies (Maxi-Mini) | Strengths + Threats | Leverage strengths to minimize or avoid external threats. |
| WT Strategies (Mini-Mini) | Weaknesses + Threats | Minimize weaknesses and avoid threats (defensive strategy). |
Leveraging AI for Instant Strategic Insights
Modern strategic planning is increasingly supported by AI modeling software. Visual Paradigm’s AI chatbot and SWOT-TOWS tools utilize natural language processing to automate the generation of these diagrams. Unlike generic AI models that simply match keywords, these tools are trained on thousands of business diagrams to understand context, semantic hierarchy, and modeling standards.
How AI Streamlines the Workflow
The AI-powered workflow addresses several pain points associated with manual analysis:
- Rapid Prototyping: By simply inputting a business name and industry context, the AI generates a foundational draft of Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats in seconds.
- Bias Reduction: AI introduces perspectives that internal teams might overlook, ensuring a more balanced view of the market landscape.
- Contextual Understanding: The system distinguishes between positive and negative attributes based on context. For example, it recognizes “strong customer base” as a Strength rather than a generic factor.
Example Workflows
Users can initiate complex analyses using simple natural language prompts:
- “Generate a SWOT Analysis Diagram for an Electric Vehicle Manufacturing Company.”
- “Prepare a SWOT Analysis Diagram for a Drone Delivery Logistics Company.”
- “Generate a SWOT Analysis Diagram for a National Museum Digital Archive Project.”
Step-by-Step Guide: Using Visual Paradigm Tools
Method 1: The AI Chatbot Approach
The AI chatbot is ideal for brainstorming and quick visualization. It allows for a conversational approach to strategy.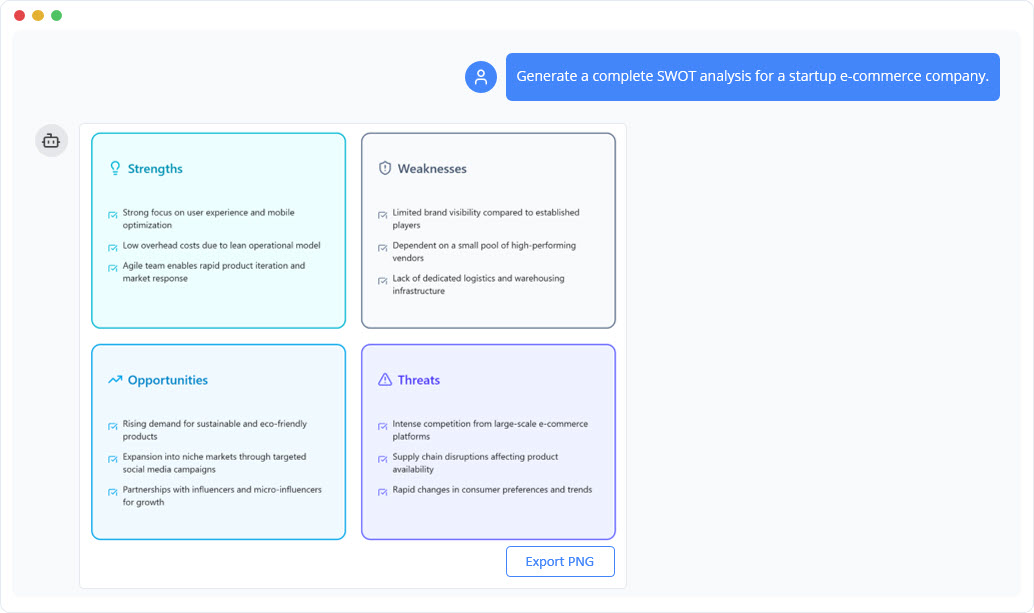
- Input Context: Describe your company, product, or challenge in the chat interface.
- Review Generation: The AI produces a structured SWOT diagram instantly.
- Iterative Refinement: Ask follow-up questions to expand on specific points (e.g., “How can we mitigate the threat of new regulations?”) or request a conversion to a TOWS matrix.
Method 2: The Structured SWOT-TOWS Tool
For a more rigorous, report-ready analysis, the dedicated SWOT-TOWS business analysis tool is recommended.
- Analyze: Enter internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats. The tool allows for the addition of evidence and impact descriptions for each factor.
- Strategize: Move to the TOWS Matrix interface to cross-reference factors and define SO, WO, ST, and WT strategies.
- Report: Generate a professional report containing an Executive Summary, detailed analysis, and conclusion. This can be exported as HTML or Markdown for easy sharing with stakeholders.
Method 3: Visual Paradigm Desktop & Online
For users requiring deep integration with other modeling languages (like UML or BPMN), the desktop and online diagramming platforms offer maximum control.
- Select Diagram > New and choose SWOT Analysis.
- Utilize the InfoArt shape to input content. This feature allows you to toggle between visual shapes and list-based editing seamlessly.
- Link SWOT elements to other diagrams, such as Use Case or Requirement diagrams, to ensure strategic alignment across the enterprise architecture.
Comparing Generic AI vs. Specialized Modeling AI
It is crucial to distinguish between general-purpose language models and those tuned for visual modeling. Visual Paradigm’s AI is specifically engineered for business frameworks.
| Feature | Generic AI Tool | Visual Paradigm AI Chatbot |
|---|---|---|
| Domain Awareness | Basic keyword matching | Contextual parsing of business logic |
| Visual Output | Often text-only or unstructured | Standardized, compliant SWOT diagrams |
| Semantic Logic | Manual classification required | Rule-based classification (e.g., distinguishing S from O) |
| Integration | Isolated output | Exportable to full modeling environments |
Conclusion
The integration of AI into strategic frameworks like SWOT and TOWS represents a significant leap forward in business analysis. By automating the data structuring process, professionals can shift their focus from formatting diagrams to interpreting insights and crafting strategy. Whether utilizing the conversational AI for quick drafts or the structured tools for comprehensive reporting, Visual Paradigm provides a robust ecosystem that ensures strategic planning is not only efficient but also deeply integrated into the broader business architecture.













